System Design Interview: 7 Ultimate Secrets to Dominate
Navigating a system design interview can feel like preparing for a marathon blindfolded. But what if you had a map? This guide reveals the ultimate strategies to not just survive but thrive in your next system design challenge.
What Is a System Design Interview?

A system design interview evaluates your ability to design scalable, reliable, and maintainable systems under real-world constraints. Unlike coding interviews that focus on algorithms, this format tests your architectural thinking, trade-off analysis, and communication skills. It’s a staple in tech giants like Google, Amazon, and Meta, where engineers must build systems serving millions.
Core Objectives of the Interview
The primary goal is to assess how well you break down complex problems. Interviewers don’t expect perfection—they want to see structured thinking. Can you ask the right questions? Identify bottlenecks? Scale a service from 1,000 to 1 million users?
- Evaluate problem-solving approach
- Test understanding of distributed systems
- Assess communication and collaboration skills
“It’s not about getting the ‘right’ answer—it’s about showing how you think.” — Career Coach, Gayle Laakmann McDowell
Common Formats and Variants
System design interviews come in various forms: high-level design (HLD), low-level design (LLD), and object-oriented design (OOD). HLD focuses on components, data flow, and scalability. LLD dives into class structures and method signatures. OOD emphasizes encapsulation and inheritance.
Some companies use take-home assignments or whiteboard sessions. Others simulate real-time collaboration using tools like Miro or Google Docs. Regardless of format, the core principles remain consistent: clarity, scalability, and trade-off awareness.
Why System Design Interviews Matter
As software systems grow in complexity, the need for engineers who can design robust architectures has never been higher. A single poorly designed component can bring down an entire platform. That’s why top tech firms invest heavily in this interview stage.
Role in Tech Hiring at Top Companies
At FAANG companies (Facebook, Amazon, Apple, Netflix, Google), system design is often the deciding factor between two equally skilled candidates. According to CareerCup, over 70% of senior engineering roles require at least one system design round.
These interviews simulate real-world scenarios engineers face daily. Can you design a URL shortener that handles 10,000 requests per second? How would you modify it for global availability? These aren’t hypotheticals—they’re job requirements.
Impact on Career Progression
Mastery of system design opens doors to senior and lead roles. Engineers who can architect systems are seen as strategic assets. They influence product direction, mentor juniors, and lead cross-functional teams.
- Higher promotion velocity
- Greater project ownership
- Increased compensation potential
According to Glassdoor data, engineers who pass system design interviews report 25% higher base salaries on average compared to those who don’t.
Core Principles of System Design
Before diving into specific designs, it’s crucial to internalize foundational principles. These act as your compass during the interview, guiding decisions when uncertainty arises.
Scalability: Handling Growth Gracefully
Scalability refers to a system’s ability to handle increased load without degradation in performance. There are two types: vertical (scaling up by adding resources to a single node) and horizontal (adding more nodes).
Horizontal scaling is preferred in modern systems due to its cost-effectiveness and fault tolerance. Techniques include load balancing, sharding, and replication. For example, a database can be sharded by user ID to distribute load evenly.
A real-world example is Twitter’s timeline service, which uses fan-out strategies to precompute timelines for users, reducing read latency during peak hours.
system design interview – System design interview menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Reliability: Ensuring Uptime and Fault Tolerance
Reliability means the system works correctly even when components fail. This involves redundancy, failover mechanisms, and monitoring.
Key strategies include:
- Replicating databases across availability zones
- Using circuit breakers to prevent cascading failures
- Implementing health checks and auto-recovery
“Design for failure. Assume everything will break.” — Werner Vogel, former CTO of Amazon
Netflix’s Chaos Monkey tool randomly terminates production instances to ensure the system remains resilient under stress.
Maintainability and Extensibility
A well-designed system should be easy to update, debug, and extend. This involves clean separation of concerns, modular architecture, and comprehensive documentation.
Microservices architecture enhances maintainability by isolating functionality into independent services. However, it introduces complexity in orchestration and monitoring, so trade-offs must be evaluated.
Google’s adoption of microservices allowed teams to deploy independently, accelerating innovation while maintaining stability.
Step-by-Step Framework for Tackling System Design Interview
Having a repeatable framework is essential. It reduces cognitive load and ensures you cover all critical aspects. Here’s a proven 6-step approach used by successful candidates.
Step 1: Clarify Requirements
Never jump into design without understanding the problem. Ask clarifying questions about:
- Functional requirements (e.g., features needed)
- Non-functional requirements (e.g., latency, availability)
- Scale (e.g., QPS, data volume)
For example, if asked to design a chat app, ask: Is it one-on-one or group chat? Do we need end-to-end encryption? What’s the expected user base?
According to Educative’s System Design Course, 40% of candidates fail because they misinterpret the scope.
Step 2: Estimate Scale
Back-of-the-envelope calculations are crucial. Estimate:
- Requests per second (RPS)
- Storage needs over 5 years
- Bandwidth consumption
Example: For a URL shortener serving 100 million users, assume 100 writes and 10,000 reads per second. With 7-character keys, storage is ~700 GB for URLs alone.
These numbers guide your choice of databases, caching layers, and CDN usage.
Step 3: Define API Contracts
Sketch high-level APIs early. This sets the interface for your system. Use REST or gRPC conventions.
system design interview – System design interview menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
For a file-sharing service:
- POST /upload → returns file ID
- GET /download/{id} → returns file
- DELETE /file/{id} → removes file
Clear APIs help structure your backend components and signal completeness to the interviewer.
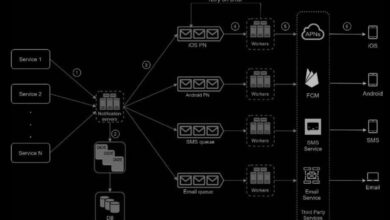
Step 4: Design High-Level Architecture
Now, draw the big picture. Identify core components:
- Load balancer
- Web servers
- Application servers
- Database (SQL/NoSQL)
- Cache (Redis/Memcached)
- Message queue (Kafka/RabbitMQ)
For a social media feed, you might have:
- Frontend → API Gateway → Feed Service → Database + Cache
- Background workers for feed generation
Use tools like diagrams.net or Excalidraw to sketch during practice.
Step 5: Dive Into Data Storage
Choose the right storage based on access patterns. Ask:
- Is data relational or hierarchical?
- Do we need strong consistency?
- What’s the read/write ratio?
For high-read, low-write systems (e.g., news feed), use NoSQL databases like Cassandra. For transactional data (e.g., payments), opt for SQL with ACID guarantees.
Consider hybrid approaches: store metadata in SQL, content in object storage (e.g., S3).
Step 6: Address Scalability and Bottlenecks
Identify potential bottlenecks:
- Database becoming a single point of failure
- Cache miss storms
- Network latency in global deployments
Solutions:
- Shard databases by user ID or region
- Use multi-level caching (browser, CDN, Redis)
- Deploy services in multiple regions with DNS-based routing
Always discuss trade-offs: eventual consistency vs. availability, cost vs. performance.
Common System Design Interview Questions
While no two interviews are identical, certain problems recur. Mastering these gives you a strong foundation.
Design a URL Shortener (e.g., TinyURL)
This classic question tests hashing, database design, and redirection logic.
Key considerations:
system design interview – System design interview menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Generating short, unique keys (Base62 encoding)
- Handling high read-to-write ratio (use cache)
- Supporting expiration and analytics
Architecture:
- API layer to generate and resolve URLs
- Database to store mappings
- Redis cache for hot URLs
- Asynchronous job for analytics
For deeper insight, see TinyURL’s engineering blog on their evolution.
Design a Chat Application (e.g., WhatsApp)
This tests real-time communication, message delivery guarantees, and scalability.
Challenges:
- Handling offline messages
- Ensuring message order
- Supporting group chats
Solutions:
- Use WebSockets or MQTT for persistent connections
- Store messages in a distributed log (Kafka)
- Implement message queuing with retry logic
For global scale, use geo-replicated databases and regional message brokers.
Design a News Feed (e.g., Facebook or Twitter)
This is one of the most complex and frequently asked questions.
Two main approaches:
- Pull model: Fetch posts from followed users at read time (simple, but slow at scale)
- Push model: Precompute feeds and store in a cache (faster reads, higher storage cost)
Hybrid approach: Use push for active users, pull for inactive ones.
Twitter uses a fan-out-on-write strategy for power users and fan-out-on-read for others, balancing latency and cost.
Advanced Topics in System Design Interview
For senior roles, expect deeper dives into distributed systems concepts.
Distributed Caching Strategies
Caching is critical for performance. But naive caching can cause problems.
Strategies:
- Cache-aside: App checks cache before DB
- Write-through: Data written to cache and DB simultaneously
- Write-behind: Data written to cache, then asynchronously to DB
Challenges:
system design interview – System design interview menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Cache invalidation (the hardest problem in CS)
- Hot keys causing node overload
- Stale data during network partitions
Solution: Use consistent hashing for sharding, and TTLs with refresh-ahead policies.
Database Sharding and Replication
Sharding splits data across machines. Replication copies data for availability.
Sharding methods:
- Range-based (e.g., user IDs 1–1M on shard A)
- Hash-based (e.g., MD5(user_id) % N)
- Directory-based (lookup table maps keys to shards)
Replication types:
- Master-slave: One writer, multiple readers
- Multi-master: Multiple writers (risk of conflicts)
Google Spanner uses TrueTime API to achieve external consistency across shards globally.
Microservices vs Monolith: Trade-offs
Microservices offer agility but increase operational complexity.
Pros of microservices:
- Independent deployment
- Technology diversity per service
- Scalability per component
Cons:
- Network latency
- Distributed tracing needed
- Eventual consistency challenges
Monoliths are simpler to develop and deploy but harder to scale and maintain as they grow.
Amazon migrated from a monolith to microservices in 2001, enabling rapid innovation and scalability.
How to Prepare for a System Design Interview
Preparation is not about memorizing designs—it’s about building intuition and practice.
Study Resources and Books
Start with foundational texts:
- Designing Data-Intensive Applications by Martin Kleppmann — The bible of modern system design
- System Design Interview – An Insider’s Guide by Alex Xu — Practical, interview-focused
- Site Reliability Engineering by Google SRE team — Real-world operations insights
Online platforms:
- Grokking the System Design Interview
- ByteByteGo — Visual system design guides
- LeetCode system design section
Practice with Real-World Scenarios
Simulate actual interviews. Use a timer and whiteboard (physical or digital).
system design interview – System design interview menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Practice problems:
- Design Instagram
- Design Uber
- Design a rate limiter
- Design a distributed ID generator
Record yourself explaining the design. Playback to assess clarity and structure.
Mock Interviews and Feedback
Nothing beats real feedback. Platforms like Pramp, Interviewing.io, and TechLead offer peer or expert mock interviews.
Focus on:
- Communication: Speak clearly and narrate your thought process
- Asking questions: Show curiosity and depth
- Handling ambiguity: Adapt when requirements change mid-interview
One engineer reported improving from “barely passing” to “strong hire” after just five mock interviews.
Mistakes to Avoid in System Design Interview
Even strong candidates falter due to avoidable errors.
Skipping Requirement Gathering
Jumping straight into architecture without clarifying scope is the #1 mistake.
Example: Designing a global video streaming service without asking about regional availability or content type leads to over-engineering.
Always start with: “Can I clarify the requirements?”
Ignoring Trade-offs
Picking a technology without justifying it is dangerous.
Saying “I’ll use Kafka” without explaining why (e.g., durability, replayability) shows lack of depth.
Instead: “I recommend Kafka because we need message durability and the ability to reprocess data during failures.”
“There are no right answers, only better trade-offs.” — Martin Kleppmann
Overcomplicating the Design
Some candidates throw in every technology they know: Kubernetes, Kafka, Redis, GraphQL, etc.
Interviewers prefer simplicity. Start simple, then scale.
system design interview – System design interview menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Example: Begin with a monolith and one database. Then discuss scaling only when prompted.
As Einstein said, “Make things as simple as possible, but not simpler.”
What is the most common system design interview question?
The most common question is designing a URL shortener (like TinyURL). It’s popular because it covers hashing, database design, caching, and API design—all fundamental concepts in a compact problem.
How long should I prepare for a system design interview?
Most engineers need 4–8 weeks of dedicated preparation. Beginners should start with 8 weeks, spending 1–2 hours daily on concepts and practice. Senior engineers with experience may need only 2–3 weeks for review.
Do I need to know coding for a system design interview?
Not extensively. You won’t write full programs, but you may sketch API endpoints, class structures, or pseudocode. The focus is on architecture, not syntax.
What tools can I use during the interview?
Most companies allow digital whiteboards (Miro, Google Jamboard) or shared documents. Some use CoderPad for collaborative design. Practice using these tools beforehand.
How important is drawing diagrams?
Extremely. A clear diagram helps the interviewer follow your logic. Use standard notations: boxes for services, arrows for data flow, clouds for external systems. Label components clearly.
Mastering the system design interview is a journey, not a sprint. It requires understanding core principles, practicing real problems, and refining communication. By following the framework outlined—clarifying requirements, estimating scale, designing APIs, and addressing bottlenecks—you position yourself as a strategic thinker. Remember, the goal isn’t to build a perfect system but to demonstrate structured, scalable, and thoughtful design. With consistent practice and the right resources, you can confidently tackle any system design challenge and turn it into your career breakthrough.
system design interview – System design interview menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: